Cause:
It is a result of complex interaction of genes, environmental triggers and hormonal changes that the immune system starts attacking on self tissues and causes inflammation of the joint. While genes do determine our inflammatory responses, it is not the only cause. Most patients who have rheumatoid arthritis do not have a family history of RA. At the same time we notice more relatives of patients have this disease and familial clustering is seen. Women are prone to RA during certain phases such as after delivery of a child, around time of menopause, later in life around 60 years suggesting hormonal changes triggering this response. Occasionally patients develop RA after viral illness, vaccinations(very very rarely), infertlity treatment, after weight loss drugs suggesting environmental trigger in those prone for an abnormal immune response.
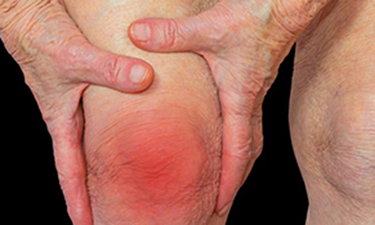
Clinical Presentation:
Joints typically affected are the fingers, wrist, shoulder and knees in the young. Older individuals may start with neck pain, knee pain and shoulder before fingers are involved. Pain starts in a single joint and progresses to the other joints over a period of 3-6 weeks. Occasionally they may move around the various joints (fleeting, palindromic) initially. Swelling is usually observed (can be missed in certain joints such as shoulder or in early diseases). Both sides of the body are symmetrically involved. While the pain may start in one joint initially, eventually 3 or more joints are inflammed. The pain occurs in the morning soon after waking up or after rest (afternoon nap). Body feels stiff for atleast 30 mins.Usually feel better as they start moving during the day and as the sun comes up. Pain again increases towards evening and patient has difficulty falling asleep.
Diagnosis:
Tests and investigations are done for diagnosing this condition, to identify extent of inflammation and damage and to assess overall health of the patient which assists the doctor in giving the right doses and choosing the ideal drug for an individual patient.
Tests for Diagnosis:
Rheumatoid Factor and Anti-CCP (Cyclic cittrulinated peptide) are the two tests. ANA (for SLE), Serum uric acid (for gout), Serum TSH (for thyroid disease) may be done to identify other diseases that can present similarly.
To identify extent and damage:
ESR and CRP gives us an idea about the severity of the inflammation. X’rays for identifying bone damage (erosions, periarticular osteopenia) may be ordered (I personally don’t do them). Occasionally ultrasound and power doppler and MRI are performed for a detailed look.
To assess overall health:
Serum creatinine to assess the kidney function, blood sugar, complete blood count are routinely performed. Liver function tests, tests for hepatitis B and hepatitis C may be required prior to starting certain medications as per the clinicians discretion.
Treatment:
Several effective and relatively safe medications are available for treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis. Today the options are much more than what we had 20-30 years ago. However the image and anxiety of kidney failure, liver failure makes patient hesitant to take the treatment. Today investigations are available at your doorstep. Liver and kidney can be closely monitored. The medical community has also learnt a lot more on how to administer drugs and monitor them (Thanks to the great work of researchers in the past and present).
I am not saying the drugs have no side effects, but the effectiveness of these drugs in preventing damage and improving the quality of life of not just the patient but the whole family outweighs the small risk associated with them. Early treatment gets the disease under control faster and with fewer deformities. Also less powerful medications (hence less side effects) and fewer medications is adequate. Treatment is broadly divided into 2. One group of medications reduce inflammation and pain. These are steroids and non steroidal anti-inflamatory drugs (NSAID) popularly known as pain killers. These effectively reduce inflammation and pain and works fairly quickly. They are usually used in the early stages to get the inflammation under control. Intermittent use may also be required in the majority and short term use in an otherwise normal individual is fairly safe. Paracetamol and tramadol are medications that reduce pain with lesser effects on inflammation.The second group is called DMARD: Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs.These medications alter the immune response and hence reduce joint swelling and damage.
They take some time to work (2-6 months)and was previously called slow acting drugs. It is important to remember this and not get disheartened if the expected pain relief is not seen in 1-3 months. NSAIDs and Steroids are usually used therefore for these early months to control inflammation until the onset of action of the DMARDs. The commonly used drugs are hydroxychloroquine sulfate, Sulfasalazine, Methotrexate, leflunamide. Injections (known as biologics) such as etanercept, infliximab, abatacept, rituximab,tocilizumab are available in India. For more information about the drugs and their side effects please check the about individual drug section.
